Understanding Osseous Surgery: A Guide to Healthy Gums and Strong Teeth
Gum disease is one of the most common oral health issues, affecting millions worldwide. Left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss, bone deterioration, and other serious complications. While regular cleanings and periodontal therapy can manage early-stage gum disease, advanced cases may require a more precise intervention known as osseous surgery.
This procedure is designed to treat severe periodontal disease by reshaping the bone around the teeth, eliminating pockets of infection, and creating a stable foundation for gum and tooth health.
What Is Osseous Surgery?
Osseous surgery is a type of periodontal surgery aimed at correcting damage caused by advanced gum disease. It involves:
- Removing diseased gum tissue
- Reshaping the underlying bone structure
- Reducing deep periodontal pockets that harbor bacteria
By carefully adjusting the bone and gum tissue, the procedure prevents further bone loss, promotes gum reattachment, and helps maintain healthy teeth for the long term.
Key Benefits of Osseous Surgery
Understanding the benefits can help patients make informed decisions about their oral health:
- Prevents Tooth Loss: Stabilizes teeth affected by bone and gum damage.
- Reduces Infection Risk: Removes pockets where harmful bacteria accumulate.
- Promotes Gum Reattachment: Helps gums fit snugly around teeth for better protection.
- Improves Oral Function: Restores bite and chewing efficiency.
- Enhances Smile Appearance: Corrects uneven gum lines caused by periodontal disease.
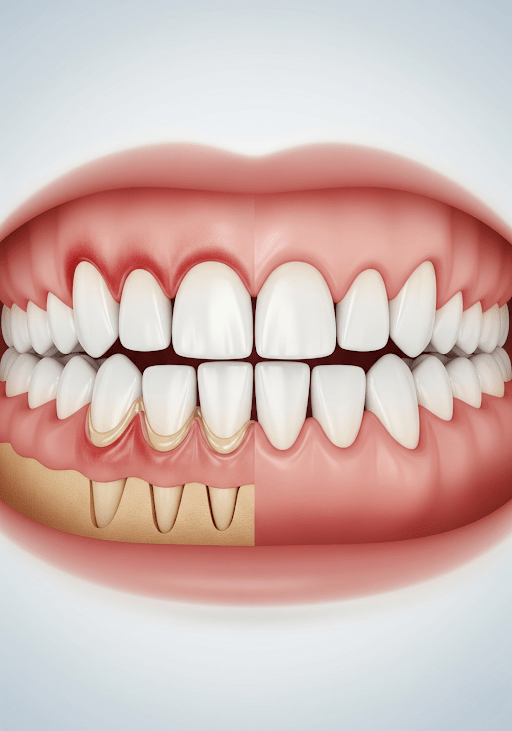
Types of Periodontal Disease Treated
Osseous surgery is particularly effective for:
- Chronic Periodontitis: Long-term gum inflammation that leads to gum recession and bone loss.
- Aggressive Periodontitis: Rapid bone and gum deterioration, often seen in younger patients.
- Pocket Formation: Deep gum pockets that harbor bacteria and cannot be managed with scaling or root planing alone.
Addressing these conditions with osseous surgery can prevent the progression of periodontal disease and protect teeth from becoming loose or lost.
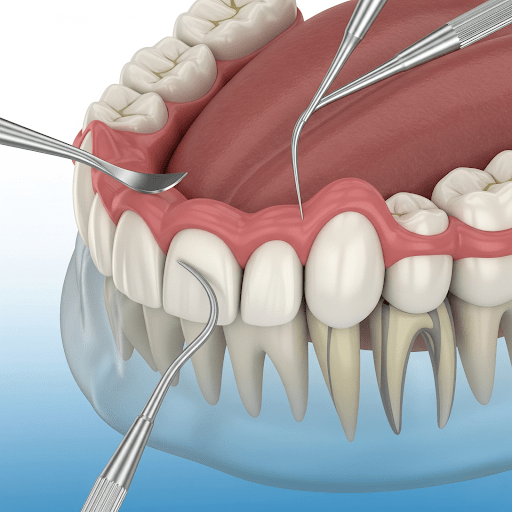
How the Procedure Works
The procedure is precise and typically performed under local anesthesia to ensure comfort. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
- Initial Examination and Imaging
Dentists perform X-rays or 3D scans to assess bone loss and determine the best surgical plan. - Gum Tissue Flap Creation
Small incisions allow the gums to be gently lifted, exposing the underlying bone and roots. - Bone Reshaping and Cleaning
Diseased bone is smoothed, and bacteria-infected pockets are cleaned to prevent further damage. - Gum Tissue Repositioning
The gums are sutured back in place to fit tightly around teeth, minimizing future pockets. - Recovery and Healing
Proper oral hygiene and follow-up care are essential for optimal results and long-term gum health.
Patients often describe the process as smooth and life-changing, with minimal discomfort compared to traditional methods.
Who Can Benefit From Osseous Surgery?
Patients with advanced periodontal disease, deep gum pockets, or bone loss are prime candidates for osseous surgery. Ideal candidates:
- Have persistent deep gum pockets despite non-surgical therapy
- Experience gum recession or bone deterioration
- Are committed to maintaining oral hygiene post-surgery
A thorough evaluation ensures the procedure is safe and effective for each individual.
Key Advantages:
Stabilizes Teeth: Corrects uneven gum lines for a healthier-looking smile.
Reduces Infection: Eliminates bacteria-prone pockets around the gums.
Enhances Gum Attachment: Gums reattach firmly to teeth for long-term protection.
Improves Oral Function: Restores chewing efficiency and bite alignment.
Boosts Aesthetic Appearance: Corrects uneven gum lines for a healthier-looking smile.
Recovery Tips and Aftercare
Post-surgery care plays a crucial role in the success of osseous surgery. Some essential tips include:
- Maintain a soft diet for the first few days.
- Avoid smoking or tobacco products during healing.
- Use prescribed mouth rinses to reduce bacterial buildup.
- Follow up with scheduled dental visits to monitor healing.
- Brush and floss gently around treated areas to prevent irritation.
Long-Term Care and Maintenance
Osseous surgery provides a long-term solution for advanced periodontal disease, but ongoing maintenance is essential:
- Schedule professional cleanings every 3–4 months
- Maintain consistent brushing and flossing habits
- Monitor for early signs of gum inflammation or infection
- Follow your dentist’s recommendations for preventive care
With diligent care, patients can enjoy healthy teeth and gums, preserve natural dentition, and prevent the recurrence of periodontal issues.
Why Osseous Surgery Matters
Advanced gum disease can silently damage bone and gum tissue, making it difficult to reverse the effects with routine dental care. Osseous surgery addresses the root causes of periodontal problems, offering:
- Long-term protection against tooth loss
- A healthier oral environment that supports strong teeth
- Improved overall confidence and oral function
With proper care and follow-up, patients can enjoy a stable, healthy smile for years to come.
Achieving optimal results often involves combining osseous surgery with routine professional cleanings and personalized home care. The procedure empowers patients to take control of their oral health and prevents complications that can impact overall wellness.
Patients seeking advanced periodontal care can experience the benefits of osseous surgery in Houston, TX, gaining stronger teeth, healthier gums, and renewed confidence.